40 coupon rate and yield to maturity
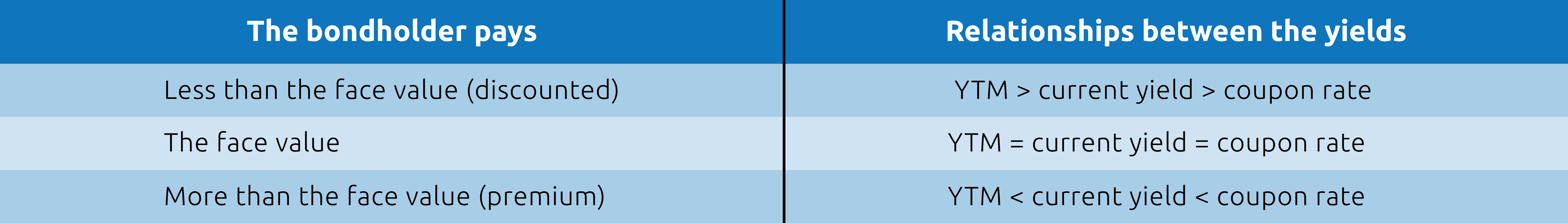
Coupon Rate Formula | Step by Step Calculation (with Examples) For example, if a bond with a face value of $1,000 offers a coupon rate of 5%, then the bond will pay $50 to the bondholder until its maturity. The annual interest payment will remain at $50 for the entire life of the bond until its maturity date, irrespective of the rise or fall in the bond's market value. Important Differences Between Coupon and Yield to Maturity - The Balance Yield to maturity will be equal to coupon rate if an investor purchases the bond at par value (the original price). If you plan on buying a new-issue bond and holding it to maturity, you only need to pay attention to the coupon rate. If you bought a bond at a discount, however, the yield to maturity will be higher than the coupon rate.
Yield to Maturity (YTM) - Overview, Formula, and Importance On this bond, yearly coupons are $150. The coupon rate for the bond is 15% and the bond will reach maturity in 7 years. The formula for determining approximate YTM would look like below: The approximated YTM on the bond is 18.53%. Importance of Yield to Maturity

Coupon rate and yield to maturity
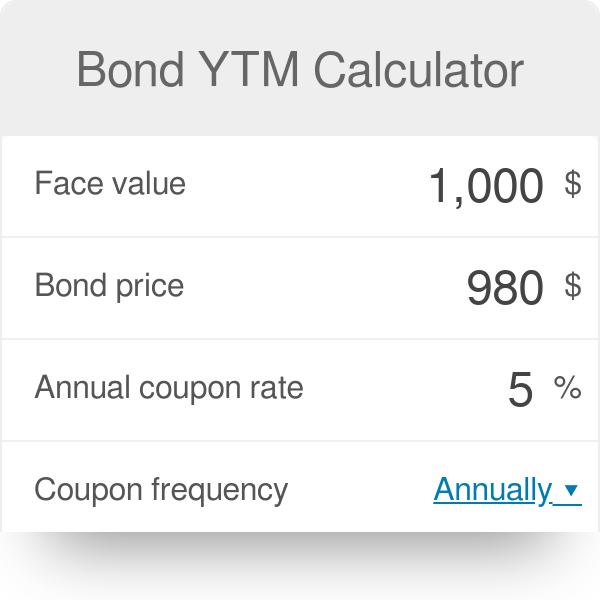
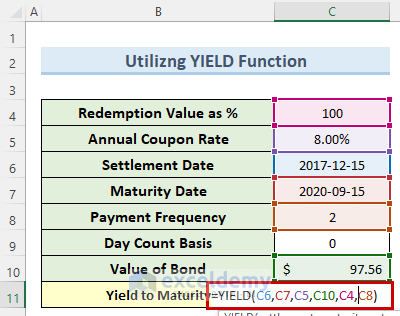
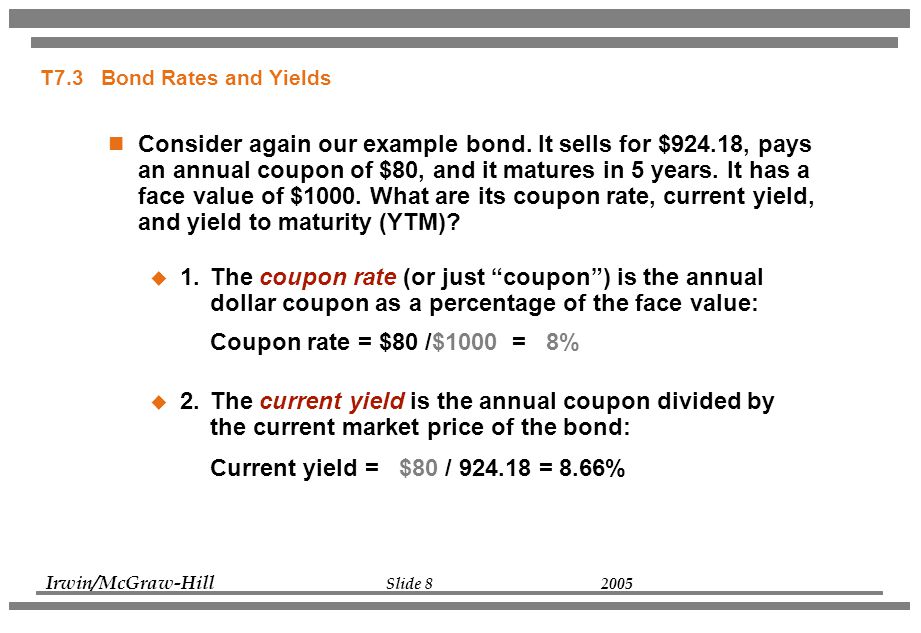
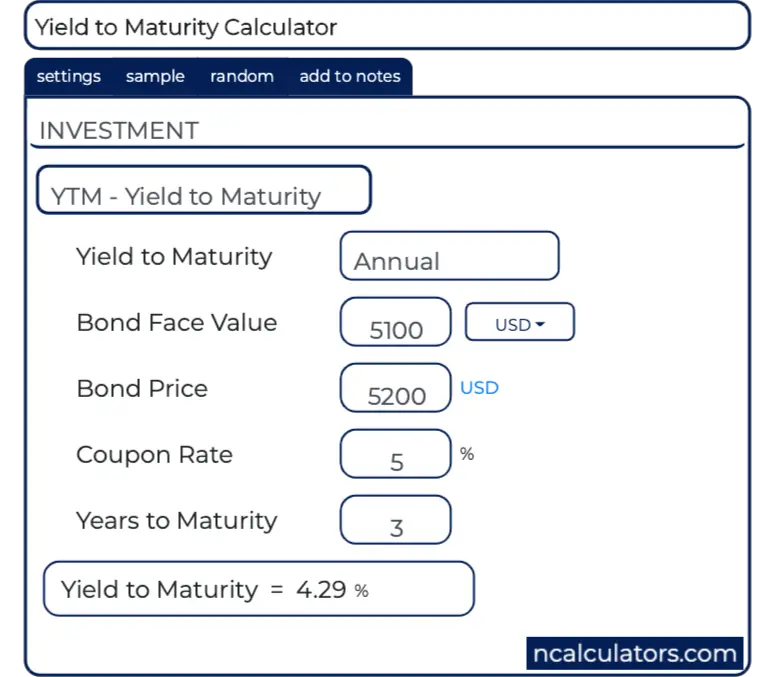
What Is a Bond Coupon, and How Is It Calculated? - Investopedia 2.4.2020 · Coupon: The annual interest rate paid on a bond, expressed as a percentage of the face value. Yield to Maturity Calculator | Good Calculators C is the periodic coupon payment, r is the yield to maturity (YTM) of a bond, B is the par value or face value of a bond, Y is the number of years to maturity. Example 2: Suppose a bond is selling for $980, and has an annual coupon rate of 6%. It matures in five years, and the face value is $1000. What is the Yield to Maturity? Concept 82: Relationships among a Bond's Price, Coupon Rate, Maturity ... Percentage price change is more when discount rate goes down than when it goes up by the same amount. Relationship with coupon rate. A bond is priced at a premium above par value when the coupon rate is greater than the market discount rate. A bond is priced at a discount below par value when the coupon rate is less than the market discount rate.
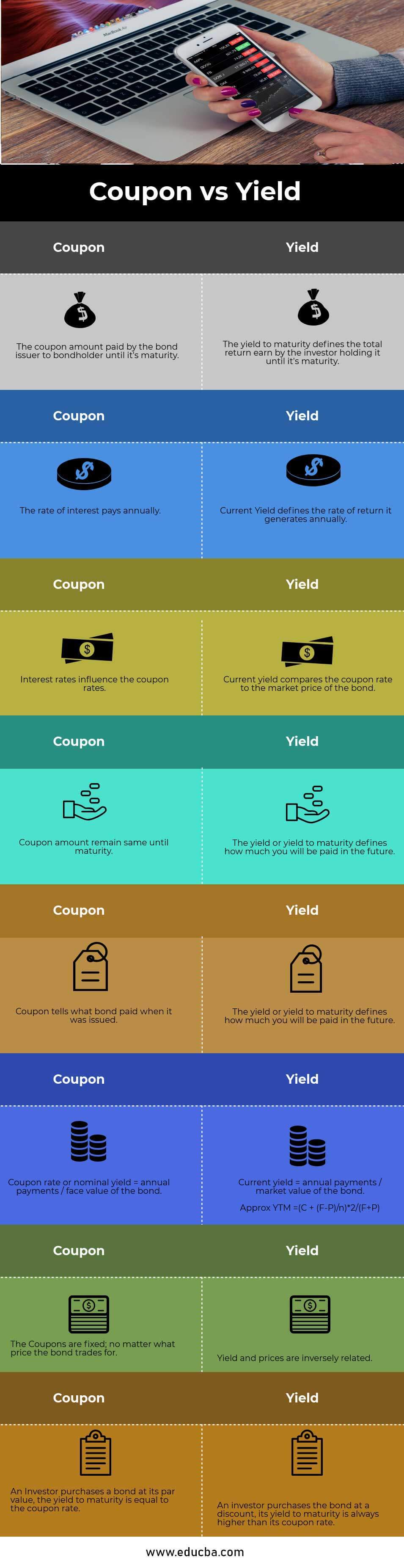
Coupon rate and yield to maturity. Coupon Rate of a Bond (Formula, Definition) - WallStreetMojo The coupon rate of a bond can be calculated by dividing the sum of the annual coupon payments by the par value of the bond and multiplied by 100%. Therefore, the rate of a bond can also be seen as the amount of interest paid per year as a percentage of the face value or par value of the bond. Mathematically, it is represented as, Coupon Rate ... Coupon vs Yield | Top 8 Useful Differences (with Infographics) - EDUCBA 3. Interest rates influence the coupon rates. The current yield compares the coupon rate to the market price of the bond. 4. The coupon amount remains the same until maturity. Market price keeps on fluctuating, better to buy a bond at a discount which represents a larger share of the purchase price. 5. Understanding Coupon Rate and Yield to Maturity of Bonds To translate this to quarterly payment, first, multiply the Coupon Rate net of 20% final withholding taxes by the face value (1.900% x 1,000,000). Then, divide the resulting annual amount by 4. Here's a sample of how you can compute your expected coupon income from your bond: Php 4,750.00 is the income you can expect to receive quarterly. What Is the Coupon Rate of a Bond? - The Balance 18.11.2021 · Rather, zero coupon bonds are sold at a discount to their value at maturity. Maturity dates on zero coupon bonds tend to be long term, often not maturing for 10, 15, or more years. ... In other words, the current yield is the coupon rate times the current price of the bond.
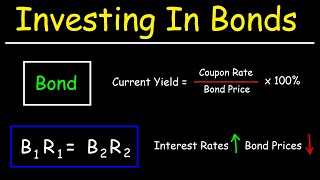
Yield to Maturity | Formula, Examples, Conclusion, Calculator The approximate yield to maturity of this bond is 11.25%, which is above the annual coupon rate of 10% by 1.25%. You can then use this value as the rate (r) in the following formula: C = future cash flows/coupon payments r = discount rate (the yield to maturity) F = Face value of the bond n = number of coupon payments Coupon Rate - Meaning, Calculation and Importance - Scripbox Know the Difference's between Coupon Rate & YTM. The main distinction between the coupon rate and YTM is the return estimation. The coupon rate payments are the same for the bond tenure. While the yield on maturity varies depending on various factors such as the number of years till maturity and the current trading price of the bond. Interest Rate Statistics | U.S. Department of the Treasury NOTICE: See Developer Notice on changes to the XML data feeds. Daily Treasury PAR Yield Curve Rates This par yield curve, which relates the par yield on a security to its time to maturity, is based on the closing market bid prices on the most recently auctioned Treasury securities in the over-the-counter market. The par yields are derived from input market prices, which are … Bond Yield Rate vs. Coupon Rate: What's the Difference? - Investopedia To understand the full measure of a rate of return on a bond, check its yield to maturity. Yield Rate A bond's yield can be measured in a few different ways. The current yield...
Understanding Bond Prices and Yields - Investopedia 28.6.2007 · As the price of a bond increases or decreases, the true yield will change—straying from the coupon rate to make the investment more or less enticing to investors. All else equal, when a bond's ... Yield to Maturity (YTM): What It Is, Why It Matters, Formula 31.5.2022 · Yield to maturity (YTM) is the total return anticipated on a bond if the bond is held until it matures. Yield to maturity is considered a long-term bond yield , but is expressed as an annual rate ... Yield to Maturity (YTM) - Meaning, Formula & Calculation - Scripbox Yield To Maturity (YTM) Formula Below is the YTM formula- yield to maturity formula Where, bond price = the current price of the bond. Coupon = Multiple interests received during the investment horizon. These are reinvested back at a constant rate. Face value = The price of the bond set by the issuer. Bond (finance) - Wikipedia In finance, a bond is a type of security under which the issuer owes the holder a debt, and is obliged – depending on the terms – to repay the principal (i.e. amount borrowed) of the bond at the maturity date as well as interest (called the coupon) over a specified amount of time.The interest is usually payable at fixed intervals: semiannual, annual, and less often at other periods.
Yield to maturity - Wikipedia The yield to maturity (YTM), book yield or redemption yield of a bond or other fixed-interest security, such as gilts, is an estimate of the total rate of return anticipated to be earned by an investor who buys a bond at a given market price, holds it to maturity, and receives all interest payments and the capital redemption on schedule. It is the (theoretical) internal rate of return …
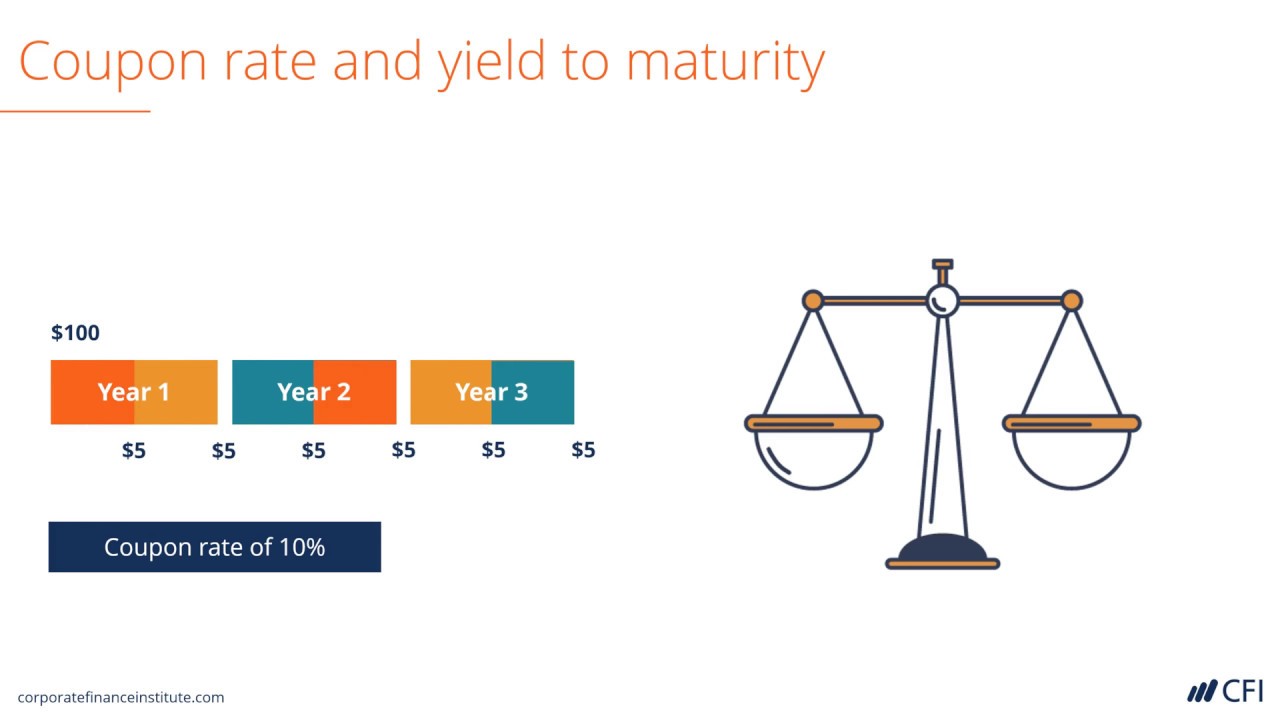
What Is Coupon Rate and How Do You Calculate It? - SmartAsset 26.8.2022 · Bond Coupon Rate vs. Interest. Coupon rate could also be considered a bond’s interest rate. In our example above, the $1,000 pays a 10% interest rate. Investors use the phrase “coupon rate” for two reasons. First, a bond’s interest rate can often be confused for its yield rate, which we’ll get to in a moment.
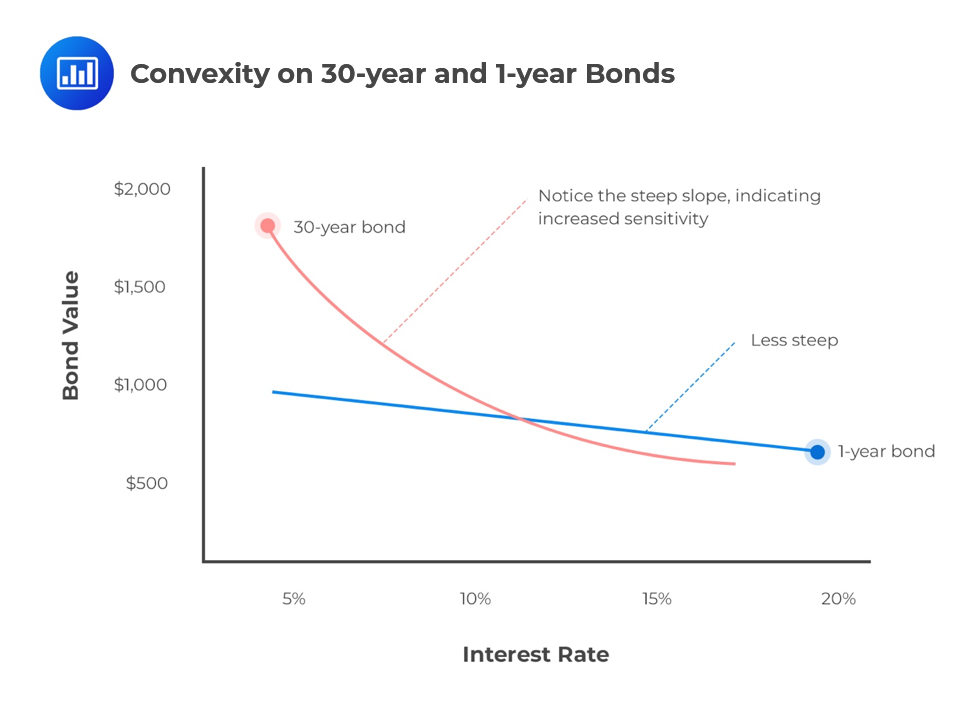
Assume both yield to maturity and coupon rate are 5. Assume both yield to maturity and coupon rate are constant through time. As time goesby, the price premium of a premium bond would gradually: A) Increase B) Decrease C) Increase then decrease D) None of the above. 6. With other conditions unchanged, the price sensitivity of a bond to changes in interest rate is higher, when: A) the bond has ...
Coupon Rate and Yield to Maturity | How to Calculate Coupon Rate The coupon rate represents the actual amount of interest earned by the bondholder annually while the yield to maturity is the estimated total rate of return of a bond, assuming that it is...
Difference between Coupon Rate And Yield To Maturity The yield to maturity (YTM) is the rate of return that an investor earns when he holds the bond till the maturity date. The YTM becomes relevant only when an investor buys a bond from the secondary market. To calculate the yield to maturity of a bond, the following formula is used. YTM = { (annual interest payment) + [ (face value - current ...
Coupon Rate - Meaning, Example, Types | Yield to Maturity Comparision Coupon Rate = 5-Year Treasury Yield + .05% So if the 5-Year Treasury Yield is 7%, then the coupon rate for this security will be 7.5%. Now, if this coupon is revised every six months and after six months, the 5-Year Treasury Yield is 6.5%, then the revised coupon rate will be 7%.
Difference Between Coupon Rate And Yield Of Maturity - Nirmal Bang The major difference between coupon rate and yield of maturity is that coupon rate has fixed bond tenure throughout the year. However, in the case of the yield of maturity, it changes depending on several factors like remaining years till maturity and the current price at which the bond is being traded.
Yield to Maturity vs. Coupon Rate: What's the Difference? 20.5.2022 · The yield to maturity (YTM) is the percentage rate of return for a bond assuming that the investor holds the asset until its maturity date. It is the sum of all of its remaining coupon payments. A ...
Bond Yield to Maturity (YTM) Calculator - DQYDJ This makes calculating the yield to maturity of a zero coupon bond straight-forward: Let's take the following bond as an example: Current Price: $600. Par Value: $1000. Years to Maturity: 3. Annual Coupon Rate: 0%. Coupon Frequency: 0x a Year. Price =. (Present Value / Face Value) ^ (1/n) - 1 =.
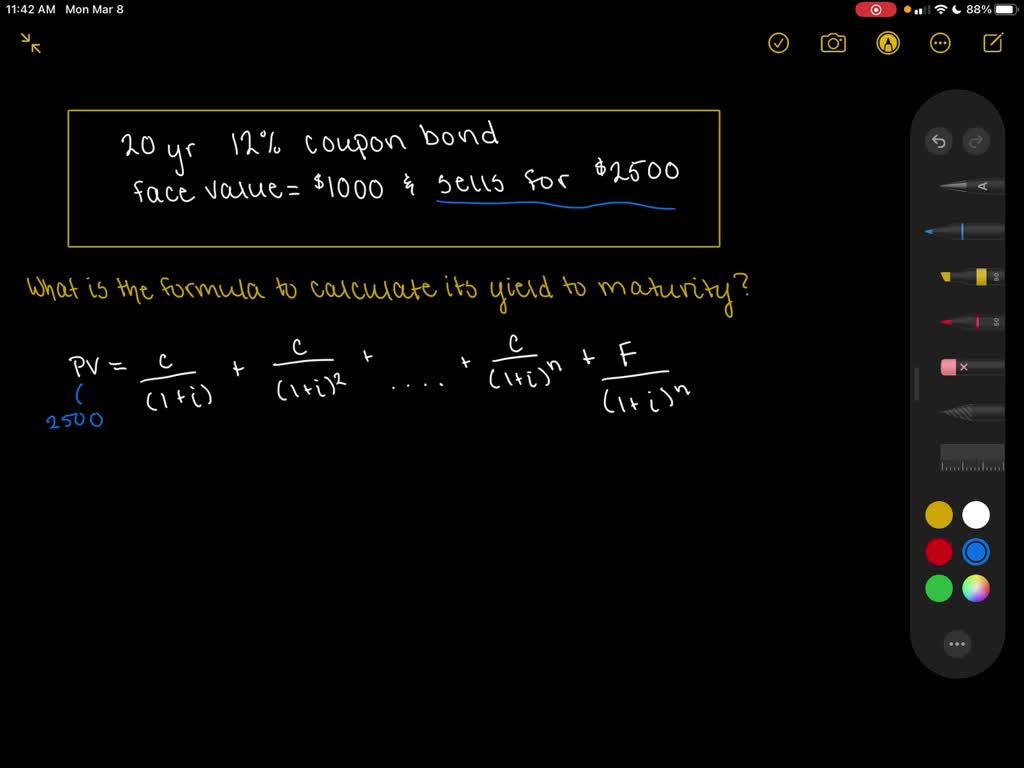
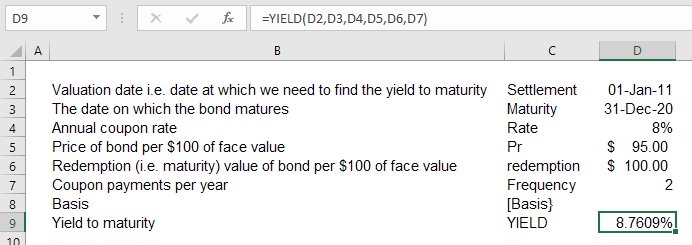
Write down the formula that is used to calculate the yield to maturity on a twenty-year 12 % coupon bond with a 1,000 face value that sells for 2,500.
Basics Of Bonds - Maturity, Coupons And Yield - InCharge Debt Solutions The coupon is always tied to a bond's face or par value and is quoted as a percentage of par. Say you invest $5,000 in a six-year bond paying a coupon rate of five percent per year, semi-annually. Assuming you hold the bond to maturity, you will receive 12 coupon payments of $125 each, or a total of $1,500.
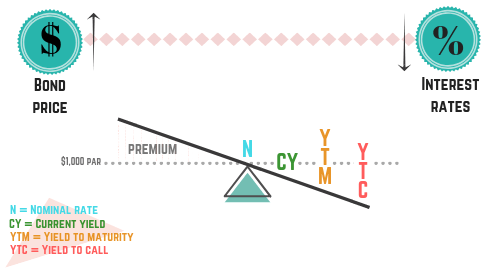
Coupon Rate - Learn How Coupon Rate Affects Bond Pricing The yield-to-maturity only equals the coupon rate when the bond sells at face value. The bond sells at a discount if its market price is below the par value. In such a situation, the yield-to-maturity is higher than the coupon rate. A premium bond sells at a higher price than its face value, and its yield-to-maturity is lower than the coupon rate.
Coupon vs Yield | Top 5 Differences (with Infographics) - WallStreetMojo Yield to maturity is the effective rate of return of a bond at a particular point in time. On the basis of the coupon from the earlier example, suppose the annual coupon of the bond is $40. And the price of the bond is $1150, then the yield on the bond will be 3.5%. Coupon vs. Yield Infographic
Current Yield vs. Yield to Maturity - Investopedia This is especially helpful for short-term investments . For example, if an investor buys a 6% coupon rate bond (with a par value of $1,000) for a discount of $900, the investor earns annual...
Coupon Rate Calculator | Bond Coupon What is the difference between bond coupon rate and yield to maturity (YTM)? As we said above, the coupon rate is the product of the division of the annual coupon payment by the face value of the bond. It merely represents your annual return from your bond investments and does not tell you anything about the actual return of your investments.
Current Yield vs. Yield to Maturity: What's the Difference? Yield to maturity is the rate of return of the entire bond cash flow, including the return of principal at the end of the bond term. Yield to maturity is a way to compare bonds with different market prices, coupon rates, and maturities. Formula The current yield of a bond is easily calculated by dividing the coupon payment by the price.
Difference Between Coupon Rate and Yield to Maturity The main difference between Coupon Rate and Yield to Maturity (YTM) is that Coupon Rate is the fixed sum of money that a person has to pay at face value. In contrast, Yield to Maturity (YTM) is the amount a person will retrieve after the maturation of their bonds. The Coupon Rate is said to be the same throughout the bond tenure year.
Difference Between Yield to Maturity and Coupon Rate Yield to Maturity is calculated as below. Yield to Maturity = Coupon + (Nominal Value - Price/Term to Maturity) / (Nominal Value+ Price/2) *100 Coupon Rate (refer below) Nominal value = Original/ Face Value of a bond Term to Maturity = the end date of the life of the bond by which all the interest payments and face value should be paid E.g.
Yield to Maturity (YTM) - Definition, Formula, Calculation Examples Assume that the bond's price is $940, with the face value of the bond at $1000. The annual coupon rate is 8%, with a maturity of 12 years. Based on this information, you must calculate the approximate yield to maturity. Solution: Use the below-given data for the calculation of YTM.
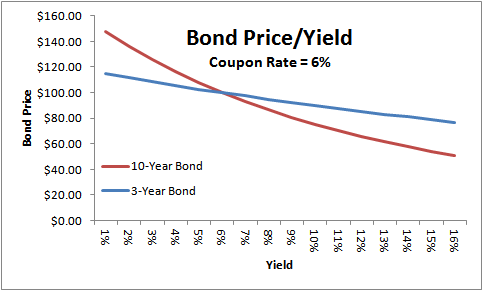
Concept 82: Relationships among a Bond's Price, Coupon Rate, Maturity ... Percentage price change is more when discount rate goes down than when it goes up by the same amount. Relationship with coupon rate. A bond is priced at a premium above par value when the coupon rate is greater than the market discount rate. A bond is priced at a discount below par value when the coupon rate is less than the market discount rate.
Yield to Maturity Calculator | Good Calculators C is the periodic coupon payment, r is the yield to maturity (YTM) of a bond, B is the par value or face value of a bond, Y is the number of years to maturity. Example 2: Suppose a bond is selling for $980, and has an annual coupon rate of 6%. It matures in five years, and the face value is $1000. What is the Yield to Maturity?
What Is a Bond Coupon, and How Is It Calculated? - Investopedia 2.4.2020 · Coupon: The annual interest rate paid on a bond, expressed as a percentage of the face value.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Yield_to_Worst_YTW_Oct_2020-01-cabc0d0cf5b64ef0b4f72afb4888b3aa.jpg)















Post a Comment for "40 coupon rate and yield to maturity"